红外与激光工程
2022, 51(5): 20220335
1 浙江工业大学信息工程学院, 浙江 杭州 310023
2 中国科学技术大学量子信息与量子科技前沿协同创新中心, 安徽 合肥 230026
3 上海交通大学区域光纤通信网与新型光通信系统国家重点实验室, 上海 200240
通过测量光热振荡周期可以检测出CaF2光学微谐振腔腔体与环境之间的热耗散率,然而多个振荡周期与热耗散率呈非线性关系,无法利用某个振荡周期值有效测量热耗散率。使用一种基于反向传播人工神经网络的传感数据测量模型,通过测量振荡周期值,实现了热耗散率的有效测量,优化了神经网络参数,提高了热耗散率测量精度。数值仿真结果表明,该方法可有效测量CaF2光学微谐振腔的热耗散率,对实现基于光学微腔的热参量探测具有重要意义。
光热振荡 热耗散率 振荡周期 人工神经网络
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, CAS, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 Synergetic Innovation Center of Quantum Information & Quantum Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
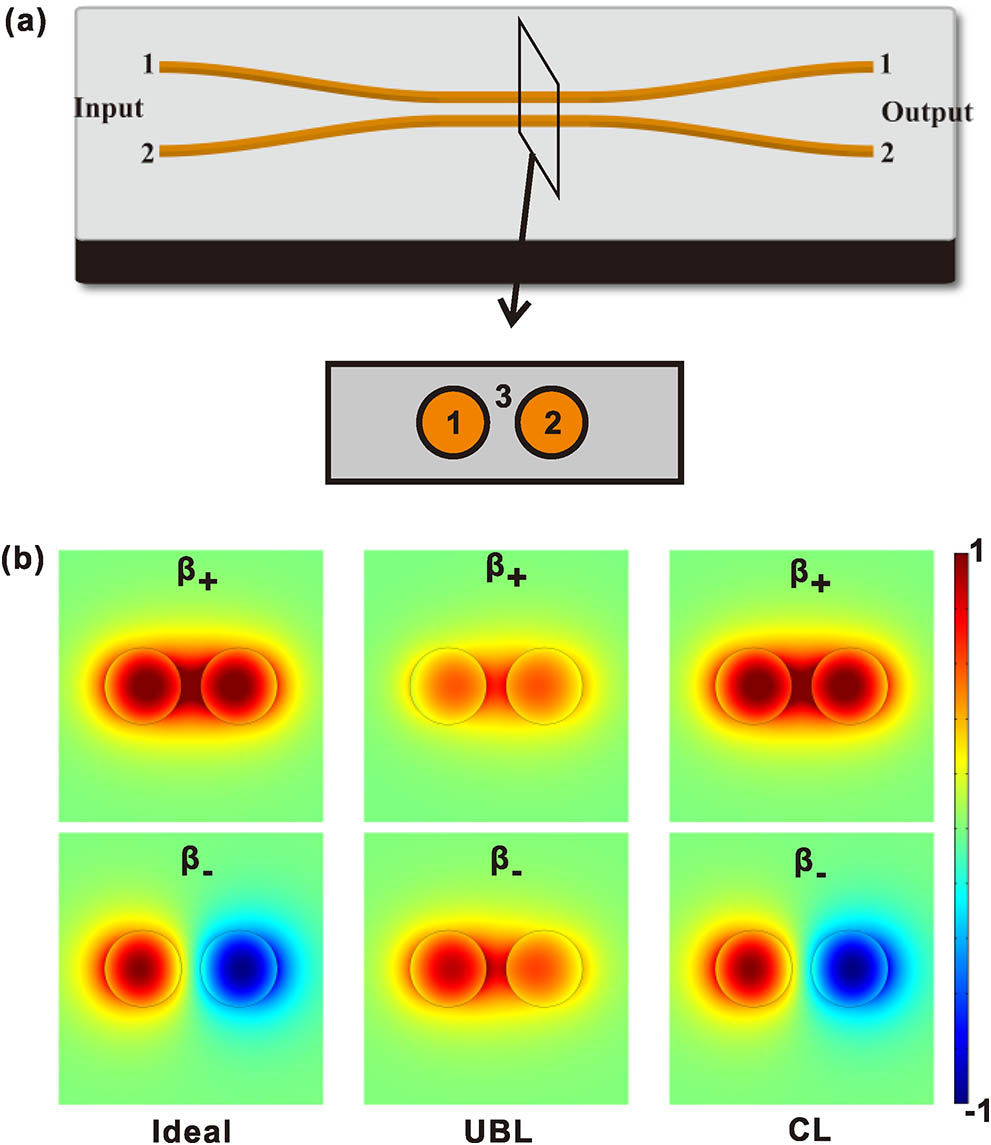
Loss is inevitable for the optical system due to the absorption of materials, scattering caused by the defects, and surface roughness. In quantum optical circuits, the loss can not only reduce the intensity of the signal, but also affect the performance of quantum operations. In this work, we divide losses into unbalanced linear losses and shared common losses, and provide a detailed analysis on how loss affects the integrated linear optical quantum gates. It is found that the orthogonality of eigenmodes and the unitary phase relation of the coupled waveguide modes are destroyed by the loss. As a result, the fidelity of single- and two-qubit operations decreases significantly as the shared loss becomes comparable to the coupling strength. Our results are important for the investigation of large-scale photonic integrated quantum information processes.
270.0270 Quantum optics Chinese Optics Letters
2017, 15(9): 092701
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Key Laboratory of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2 National Synchrotron Radiation Laboratory, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230029, China
By using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots (QDs), we study the effect of cavity quantum electrodynamics on the coupling of the microtoroid cavity. When with whispering gallery (WG) modes, the microtoroid cavity demonstrates high quality factor and small mode volume at visible wavelengths. Accordingly, fiber tapers allow QDs to adhere into the cavity and further permit the control of site-selected coupling. From the luminescence spectra, QDs are modulated effectively by cavity modes. Variable modulations are observed by changing QD coupling conditions. Therefore, based on experimental and theoretical research, strong and tunable Purcell enhancement can be realized by this system.The authors thank Jinming Cui and Chunhua Dong for their helpful discussion. This work was supported by the National Fundamental Research Program of China (No. 2006CB921900), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 60537020 and 60621064), and the Knowledge Innovation Project of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
光纤锥 微芯圆环 腔量子电动力学 量子点 020.5580 Quantum electrodynamics 140.3945 Microcavities 060.2310 Fiber optics Chinese Optics Letters
2010, 8(7): 709
Author Affiliations
Abstract
Key Lab of Quantum Information, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026E-mail: zfhan@ustc.edu.cn
Whispering gallery modes in silica microspheres are excited by a tunable continuous-wave laser through the fiber taper. Ringing phenomenon can be observed with high frequency sweeping speed. The thermal nonlinearity in the microsphere can enhance this phenomenon. Our measurement results agree very well with the theoretical predictions by the dynamic equation.
二氧化硅微球腔 振铃现象 热效应 140.3410 Laser resonators 140.4780 Optical resonators 140.6810 Thermal effects Chinese Optics Letters
2009, 7(4): 04299





